Active Directory - Backup, Restore
Knowledge Base Questions & Answers
What must be done to backup AD (Active Directory)?
System state’s data backup must be done to backup of AD.
What data contains System State?
System State contains:
-
AD (database including other files in NTDS folder) (only on DC (Domain Controller)).
-
Boot and system files.
-
DFSR (Distributed File System Replication) staging.
-
AD CS (Active Directory Certificate Services) (only if Certificate Authority server is installed).
-
Cluster Service Database (only if Failover Cluster server is installed).
-
COM+ class registration database.
-
File system junctions.
-
Group Policies settings (only on DC).
-
IIS (Internet Information Services) meta-directory (only if IIS server is installed).
-
Registry
-
Netlogon shared folders: default profiles, system policies, logon/logoff/startup/shutdown scripts.
-
SYSVOL (System Volume) folder (only on DC).
What are AD Restore types?
There are two AD Restore types:
-
Non-Authoritative Restore (D2 restore).
-
Authoritative Restore (D4 restore).
What is Non-Authoritative Restore of AD?
-
Non-Authoritative Restore is the default method to restore AD, and it is using when its data lost or corrupted.
-
It restores a DC to its state at the time of backup. After restoring of DC, the local copy of SYSVOL is compared with its replication partners. After restarting DC, SYSVOL replicates any necessary changes to itself, bringing restored DC up-to-date with the other DCs within the domain.
-
To perform a Non-Authoritative restore, DC must be started in DSRM (Directory Services Restore Mode).
What is the Authoritative Restore of AD?
-
Authoritative Restore performs restoring of DC from backup, and after making up necessary configurations, the AD marks the local SYSVOL as authoritative and replicates it to the other DCs within the domain.
-
It has abilities to restore only particular objects.
For example, if OU (Organizational Unit) was deleted. The Authoritative Restore will be able to restore just this object.
-
To perform an Authoritative restore, DC must be started in DSRM.
-
Authoritative Restores need to use ntdsutil utility.
-
Authoritative Restore often needed when human error is involved, such as when an administrator accidentally deletes some objects and that change replicated to the other DCs and the object cannot be recreated easily.
What is DSRM (Directory Services Restore Mode)?
-
DSRM is a special boot mode, which is using for repairing or recovering AD.
-
It is used to login to the computer when AD has failed or needs to be restored on DC.
Windows DNS (Domain Name System) Server - Zone
Knowledge Base Questions & Answers
What is an “AD (Active Directory) - Integrated DNS Zone”?
-
“AD (Active Directory) - Integrated DNS Zone” is a DNS zone stored within the AD database.
-
It can be updated on any DNS server and replicates updates to all DNS servers within the AD domain or forest.
-
All DNS servers running on these DCs (Domain Controllers) can act as primary servers for the zone and accept dynamic updates.
On which servers can the “AD-Integrated DNS Zone” be created?
“AD-Integrated DNS Zones” are created on DCs.
What is Aging/Scavenging?
-
Aging/Scavenging is the process that DNS servers use to identify and remove stale (outdated) resource records. Keeping the DNS database up-to-date and free from unnecessary entries that could cause resolution issues is vital.
-
The process targets dynamically created DNS records, such as those created by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) clients.
-
Static records, which are manually entered, are not affected by this process unless explicitly configured.
-
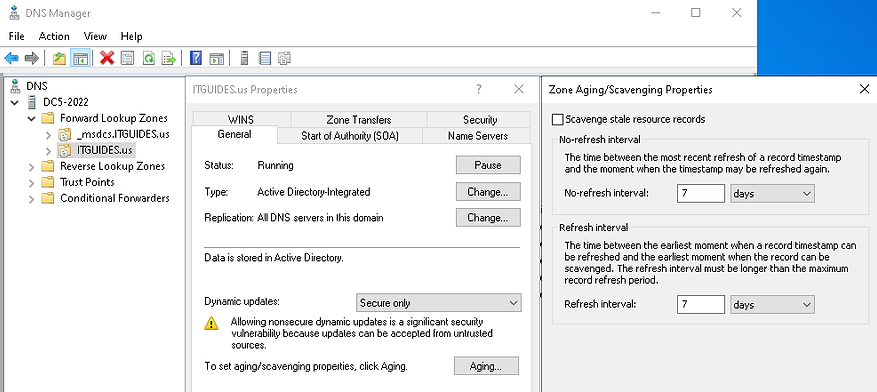
By default, Aging/Scavenging is disabled on the DNS servers. It requires explicit activation and configuration on the server, the individual zones, or both.
-
For zones, Aging/Scavenging can be configured for “Forward Lookup Zones” and “Reverse Lookup Zones.”
-
The default Aging/Scavenging period is seven days.
-
Example of default Server Aging/Scavenging properties on DNS server level.

-
Example of default zone Aging/Scavenging properties on DNS zone level.
Experience-Based/Practical Questions & Answers
How are DNS dynamic updates configured within the “DNS Manager” MMC (Microsoft Management Console) snap-in?
-
DNS dynamic updates are configured on the DNS zone levels: Forward and Reverse Lookup zones.
-
If the DNS zone is AD-Integrated, AD replication automatically enables and manages dynamic updates.
-
For “Forward Lookup Zones,” the path is as follows: “DNS Manager” MMC (Microsoft Management Console) snap-in -> DNS –> Server-Name –> “Forward Lookup Zones” -> Zone-Name -> Properties -> General tab -> “Dynamic Updates” drop-down menu.

-
For “Reverse Lookup Zones,” the path and settings are similar. You just need to open the “Reverse Lookup Zones” properties.
If DNS dynamic update is enabled, when does the refresh of the DNS record occur?
-
Computers periodically send a refresh request to the DNS server to update their DNS records.
-
The default refresh interval is typically every 24 hours but can be configured differently.
-
Certain network services, such as DHCP servers, may trigger a refresh when they renew client addresses.
How do you manually force DNS dynamic updates?
There are the following ways to do it:
-
Restart Netlogon service on Services MMC snap-in.
-
Restart computer.
-
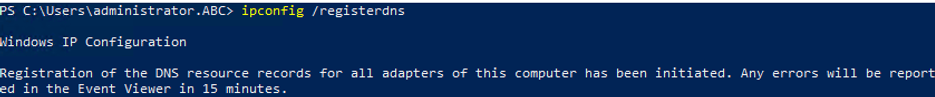
Run command:
ipconfig /registerdns
If DNS dynamic updates don’t work, what should be done to resolve the issue?
-
If a static IP (Internet Protocol) address is used on a computer, then check if the IP address of the DNS server is specified in DNS fields on network adapter properties.
-
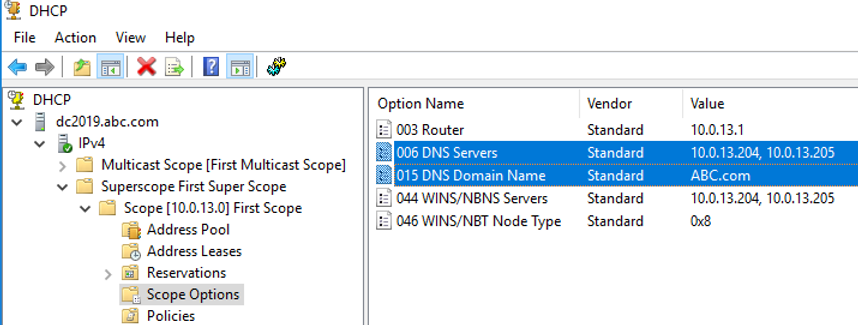
If it is a DHCP client, then check the DHCP configuration. The scope option must contain DNS servers, which the computer gets from the DHCP server.
-
Check if you can ping DCs, which are specified on DNS fields.
How can you troubleshoot typical DNS zone related issues?
To troubleshoot DNS zone related issues:
-
Check the DNS server.
-
Check the DNS zone configuration.
-
Verify DNS records.
-
Check DNS replication (if using multiple servers).
-
Check “DNS Forwarders”
-
Examine DNS cache.
-
Review DNS event logs.
-
Use DNS troubleshooting tools like nslookup.
-
Review firewall and security settings.